Fresh blood products are products that can be manufactured by simple separation of blood into its components via centrifugation. Prior to issuing product, there are a number of steps undertaken by the Australian Red Cross Lifeblood (Lifeblood) to improve the safety of the products supplied. These include:
- Mandatory testing – ABO and RhD blood type, viral screening, red cell antibody screening and syphilis testing.
- Leucodepletion – all red cells and platelets are filtered to remove white blood cells
- Bacterial contamination screening – platelets are stored at room temperature and are therefore at a greater risk of growing bacteria than other blood products. For this reason all platelets are screened for contamination.
Red blood cells
Red blood cells transport oxygen. Red cell transfusions are used for people with cancer and other blood diseases, people having surgery, people with anaemia, people during childbirth, and trauma patients. More information can be found under the 'Red cell transfusions' webpage.
The graph below illustrates how the supply trend for red cells has gone from 768,919 units in 2007-08 to 763,542 units issued in 2012-13. A reduction in red cell demand was experienced for the first time in 2012-13.
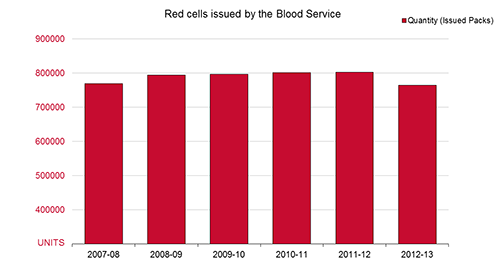
FIGURE: Red cells issued 2007-08 to 2012-13
To view the above chart and related data in Excel format download ![]() Red Blood Cells Issued by the Blood Service 2007-13 Chart and Data (xls) (40.5 KB).
Red Blood Cells Issued by the Blood Service 2007-13 Chart and Data (xls) (40.5 KB).
Platelets
Platelets are important for blood clotting and tissue repair. A low platelet count is called thrombocytopenia.
Platelet transfusions are required when patients have a low platelet count or have problems with their platelet function. These patients include people with cancer who are receiving chemotherapy, people who have a bone marrow transplant, people who take medicines that interfere with platelet function and patients who are bleeding. More information can be found in the 'I need to know about platelets' fact sheet.
The graph below illustrates how the supply trend for platelets has continued to increase from 116,665 units in 2007-08 to 134,576 units issued in 2012-13.
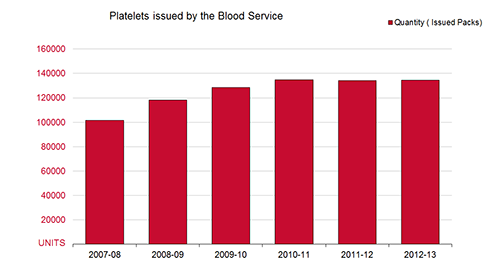
FIGURE: Platelets issued 2007-08 to 2012-13
To view the above chart and related data in Excel format download ![]() Platelets Issued by the Blood Service 2007-13 Chart and Data (xls) (40 KB)
Platelets Issued by the Blood Service 2007-13 Chart and Data (xls) (40 KB)
Plasma
Plasma is the liquid component of blood and is mostly made of water. Plasma carries blood cells and other substances around our body.
Lifeblood manufactures three plasma products as described below.
Fresh Frozen Plasma (Clinical plasma)
Plasma is the liquid component of blood. Fresh frozen plasma is used to replace clotting factors and also by patients who need to quickly reverse the effects of blood thinning medications. More information can be found in the 'I need to know about fresh frozen plasma (FFP)' fact sheet.
Cryoprecipitate
Cryoprecipitate is made from fresh frozen plasma. It contains proteins, including fibrinogen, involved in blood clotting. Cryoprecipitate is used in patient where they have a reduced level of fibrinogen, or where their fibrinogen is not working property. This may include during a trauma, or massive bleeding. More information can be found under the 'Cryoprecipitate transfusions' webpage.
Cryodepleted plasma
Cryodepleted plasma is made from fresh frozen plasma. It used most commonly in plasma exchange for patients with thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura (TTP). More information can be found under the 'Cryodepleted plasma transfusions' webpage.
Plasma for fractionation
Lifeblood also provides plasma to CSL Ltd for the manufacture of plasma derived products.

