
Scope
This document provides guidance to health providers on better practice in transfers of blood and blood products around Australia.
Additionally it offers tools that health providers can use to comply with relevant standards and accreditation.
Introduction
Under the National Blood Agreement all Governments are committed to providing an adequate, safe, secure and affordable supply of blood products, services and promoting high quality management of blood products.
This module for Blood and Blood Product Transfers aims to assist health providers in meeting the requirement of the Statement on National Stewardship Expectations for the Supply of Blood and Blood Products.1 This module will assist health providers to develop a guideline or Memorandum of Understanding (MOU) to facilitate blood and blood product transfer arrangements between providers.
The intention is for this guideline to:
- Help identify transfer options for blood and blood products between health providers, including between public and private.
- Outline how to ensure that acceptable temperature ranges for blood and blood products are maintained during transportation.
- Outline how health providers can ensure blood has been stored and transported correctly before accepting a transfer.
- Provide a uniform process for transferring blood and blood products.
- Foster a culture throughout the blood sector that strives to transfuse all units before expiry, noting that some discards are appropriate but not inevitable.
The term health provider in this document refers to an organisation providing health services to the Australian community and approved by the NBA to receive blood and/or blood products through the NBA supply contracts.
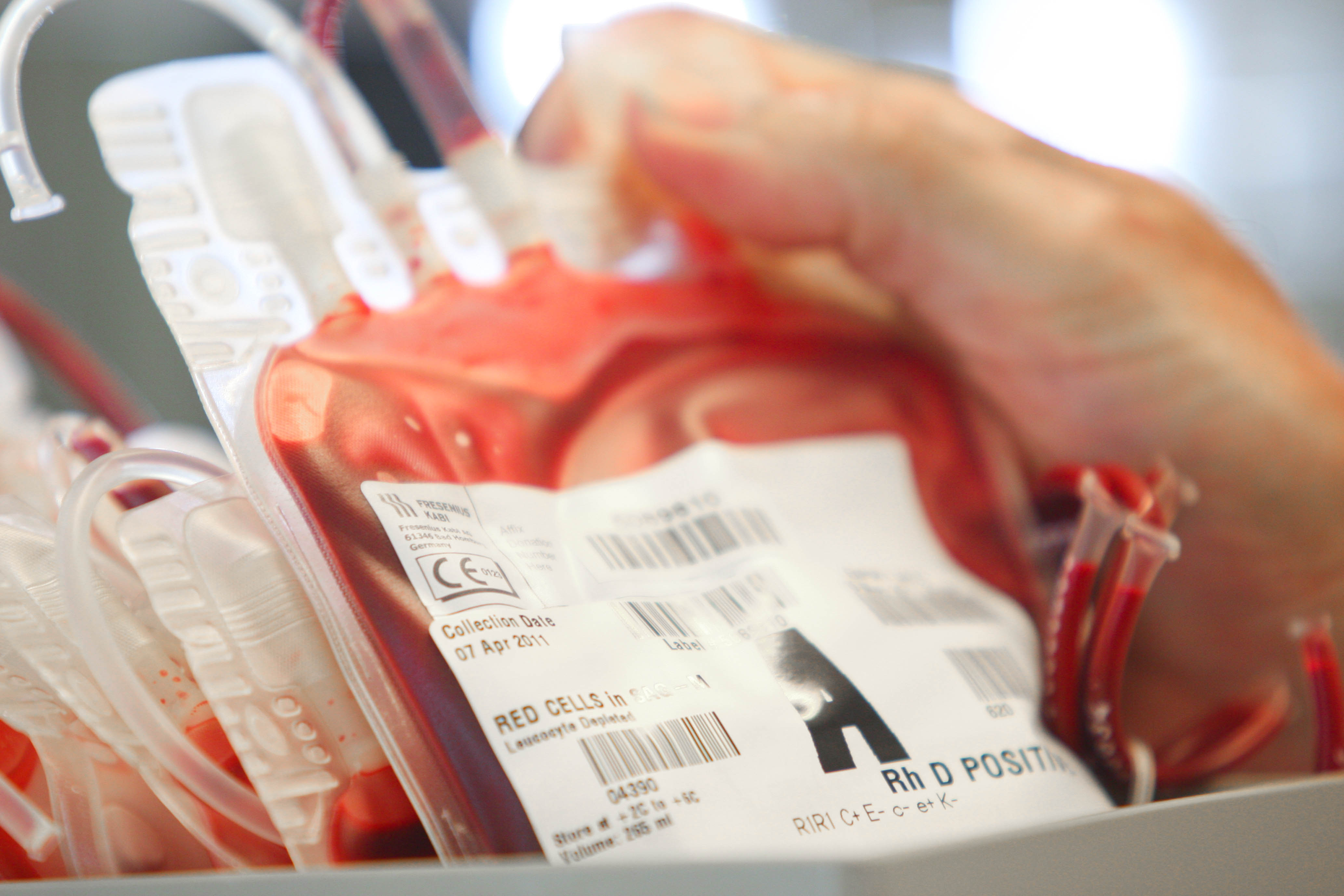
This guideline covers blood and blood products as outlined in the National Safety and Quality Health Service (NSQHS) Standard 7, Blood and Blood Products Standard2, including:
Fresh blood components
- red blood cells
- platelets
- clinical fresh frozen plasma
- cryodepleted plasma
Plasma-derived and recombinant products
- albumin
- immunoglobulins, including immunoglobulin replacement therapy (e.g. IVIg) and hyperimmune globulins
- clotting factors
Next page: Managing Blood and Blood Product Transfers: Preparation
Previous page: Tip 10 - Have a patient blood management program and Implementation

